El recorte en los presupuestos federales podría revertir el reciente progreso
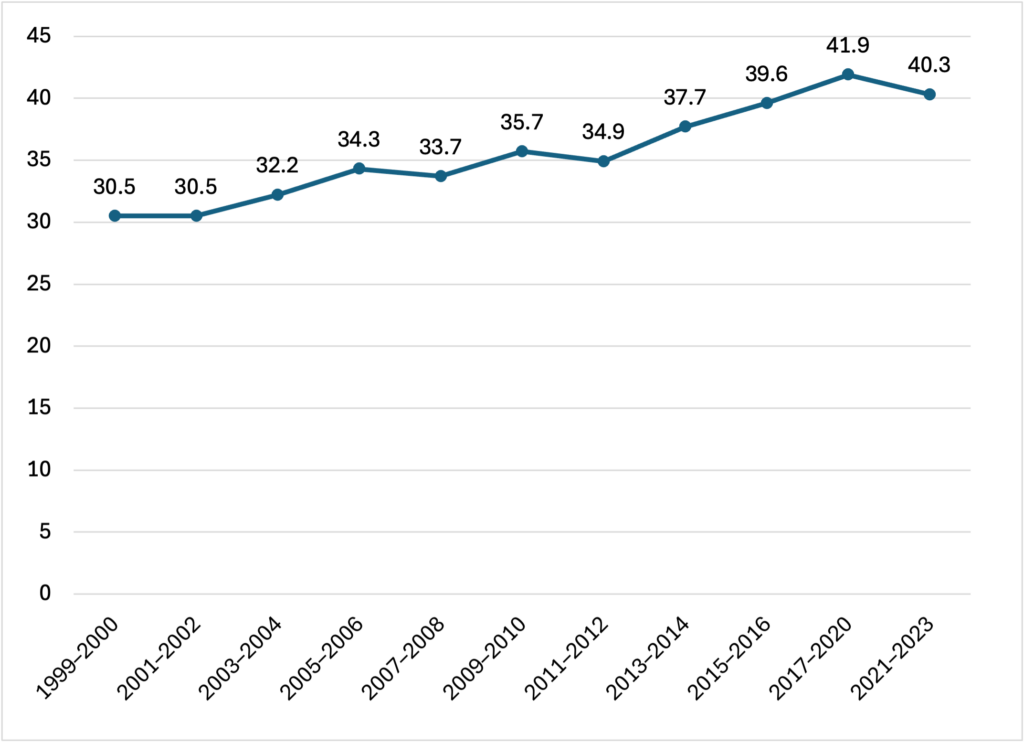
(Washington, DC – 16 de octubre de 2025) – Datos recientemente publicados revelaron que diecinueve estados tenían tasas de obesidad adulta del 35 % o más en 2024, en comparación con 23 estados el año anterior, lo que significó un descenso por primera vez del número de estados con una tasa del 35 % o superior para este conjunto de datos.
Sin embargo, este progreso está limitado y en riesgo debido en parte a las recientes acciones federales para recapturar y reducir los fondos para programas de salud pública, eliminar programas, despedir a especialistas que trabajan en la prevención de las enfermedades crónicas y limitar el acceso a los apoyos nutricionales. Esta es la conclusión a la que llega el estudio State of Obesity 2025: Better Policies for a Healthier America (“Estado de la obesidad 2025: Mejores políticas para un país más sano”) publicado hoy por Trust for America’s Health (TFAH), una organización sin fines de lucro y apartidaria dedicada a la investigación y las políticas en materia de salud pública.
La investigación, basada en parte en el análisis que TFAH hizo de datos de 2024 recientemente publicados por el Sistema de Vigilancia de los Factores de Riesgo Conductuales (BRFSS) de los Centros para el Control y la Prevención de Enfermedades, datos recientes de la Encuesta de Salud Nacional y Examen de Nutrición 2021-2023 (NHANES), muestra que, si bien la suba en el número de personas adultas con obesidad se ralentizó en algunos estados, la tasa de obesidad nacional general sigue siendo alarmantemente alta. A nivel nacional, 4 de cada 10 personas adultas tienen obesidad.
“Las barreras estructurales que obstaculizan la alimentación saludable y la actividad física necesitan continua atención por parte de las políticas públicas e inversión —expresó J. Nadine Gracia, M.D., MSCE, presidenta y directora ejecutiva de Trust for America’s Health—. Es vital que el Gobierno y otros sectores inviertan, en lugar de recortar, en programas que han demostrado que apoyan la buena nutrición y la actividad física y que aseguran que se llegue a todas las comunidades”.
Conclusiones clave incluidas en el informe:
- Los estados con mayores tasas de obesidad en personas adultas en 2024 fueron Virginia Occidental (41,4 %), Misisipi (40,4 %) y Luisiana (39,2 %) (datos de 2024 del BRFSS).
- Los estados con menores niveles de obesidad en personas adultas en 2024 fueron Colorado (25,0 %), Hawái (27,0 %) y Massachusetts (27,0 %) más Washington, D.C. (25,5 %) (datos de 2024 del BRFSS).
- Las personas adultas negras y latinas tuvieron las tasas de obesidad más altas con un 49,9 % y un 45,6 % respectivamente.
- Quienes viven en comunidades rurales tienden a tener tasas de obesidad más altas que quienes habitan en áreas metropolitanas.
- Los niveles de obesidad son típicamente más bajos entre personas con estudios universitarios y para personas en hogares con mayores ingresos, lo que sugiere que la asequibilidad de los alimentos saludables desempeñan un papel en las tasas de obesidad de la nación.
Las tasas de obesidad están aumentando en la población infantil y adolescente. Poco más del 21 % de los niños, niñas y adolescentes estadounidenses, entre los 2 y los 19 años, tienen obesidad a nivel nacional (NHANES, 2021-2023).
- Estas tasas crecieron más del triple desde mediados de la década de 1970, y la juventud negra y latina tienen índices de obesidad considerablemente más altos que sus pares de comunidades asiáticas y blancas.
La obesidad y otras enfermedades relacionadas con la dieta están asociadas con una variedad de estados de salud física y mental, mortalidad más alta, costos de salud más altos y pérdida de productividad. Si bien las tasas de obesidad dependen de muchos factores, el contexto económico y de la comunidad determinan tanto la vida diaria de la población como sus opciones con respecto a alimentos saludables, actividad física, educación, trabajo y seguridad financiera, lo cual afecta sistemáticamente el peso y la salud de las personas.
Aunque las tasas de obesidad aumentaron para todos los grupos poblacionales, los grupos con índices más altos, que incluyen a personas que viven en comunidades rurales y algunas poblaciones no blancas, típicamente enfrentan más barreras estructurales que obstaculizan la alimentación saludable, como el costo de la comida y el acceso a ella, y la falta de oportunidades y lugares para hacer actividad física en sus vecindarios.
El informe incluye un especial sobre los hallazgos científicos emergentes y las consideraciones políticas en torno a los alimentos ultraprocesados y el papel que desempeñan en la crisis de obesidad, una problemática que está atrayendo creciente atención a nivel nacional y que constituye el foco de la iniciativa Make America Healthy Again. Las autoras del estudio entrevistaron a un director de nutrición escolar de Colorado que se explayó sobre dificultades técnicas y financieras específicas asociadas con la eliminación de alimentos ultraprocesados en las comidas escolares.
El documento también resalta los programas federales que buscan hacer frente al incremento de las tasas de enfermedades crónicas como la obesidad. Sin embargo, el presupuesto presidencial para el año fiscal 2026 propone la eliminación casi total del Centro Nacional para la Prevención de Enfermedades Crónicas y Promoción de la Salud en los CDC. Entre las labores de este centro, hay programas fundamentales que financian iniciativas estatales, locales, tribales y territoriales para hacer frente y prevenir la obesidad, la diabetes, la enfermedad cardíaca, el accidente cerebrovascular y otras enfermedades crónicas.
El informe incluye recomendaciones para la acción política para la administración, el Congreso y los estados a fin de afrontar la crisis de obesidad de la nación, entre ellas:
- Conservar y fortalecer el Centro Nacional para la Prevención de Enfermedades Crónicas y Promoción de la Salud en los CDC, que apoya actividades comprobadas de prevención de enfermedades en estados y comunidades.
- Revertir los recortes efectuados y propuestos a programas de apoyo a la nutrición al tiempo que se mejora la calidad nutricional de los alimentos disponibles, incluidos Programa Asistencial de Nutrición Suplementaria (SNAP) y el Programa de Asistencia Nutricional Especial para Mujeres, Bebés y Niños (WIC).
- La Administración de Alimentos y Medicamentos debería implementar un requisito de etiquetado nutricional frontal de los envases para ayudar a la población a hacer elecciones informadas.
- Garantizar el acceso a la salud, incluidos los programas de prevención y tratamiento de la obesidad, revirtiendo los recortes a Medicaid y a los subsidios para el mercado de salud.
- Atacar los causas principales y los factores que impulsan la disparidades en la salud y dirigir los programas de prevención de la obesidad a las comunidades con mayores necesidades.
- Hacer que la actividad física sea más accesible incrementando las iniciativas fundamentadas empíricamente que apoyan el transporte activo y la actividad física en las comunidades.
- Abordar las estrategias de marketing y de precios de la industria para reducir la publicidad de alimentos poco saludables dirigida a niños y niñas.
El informe completo puede leerse en: https://www.tfah.org/report-details/state-of-obesity-report-2025
Trust for America’s Health es una organización sin fines de lucro y apartidaria dedicada a las políticas de salud pública, la investigación y la incidencia que promueve la salud óptima para cada persona y comunidad y hace de la prevención de enfermedades y lesiones una prioridad nacional.